

The Difference between a 2-stroke and a 4-stroke engine is how quickly this combustion cycle process occurs, based on the number of times the piston moves up and down during each cycle.
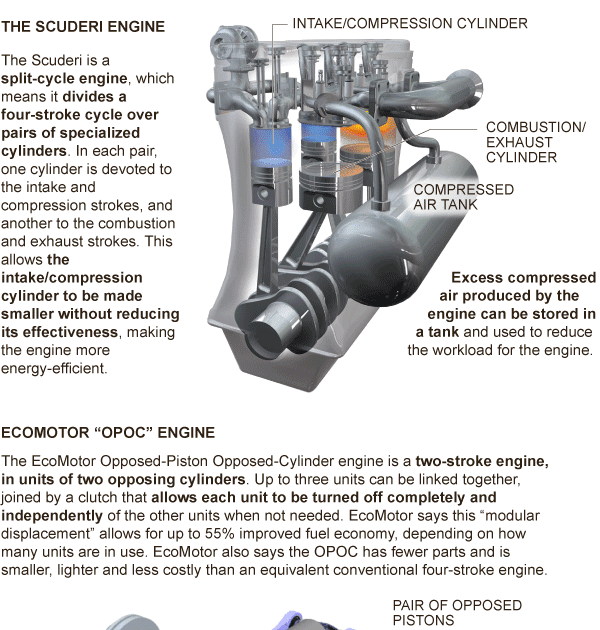
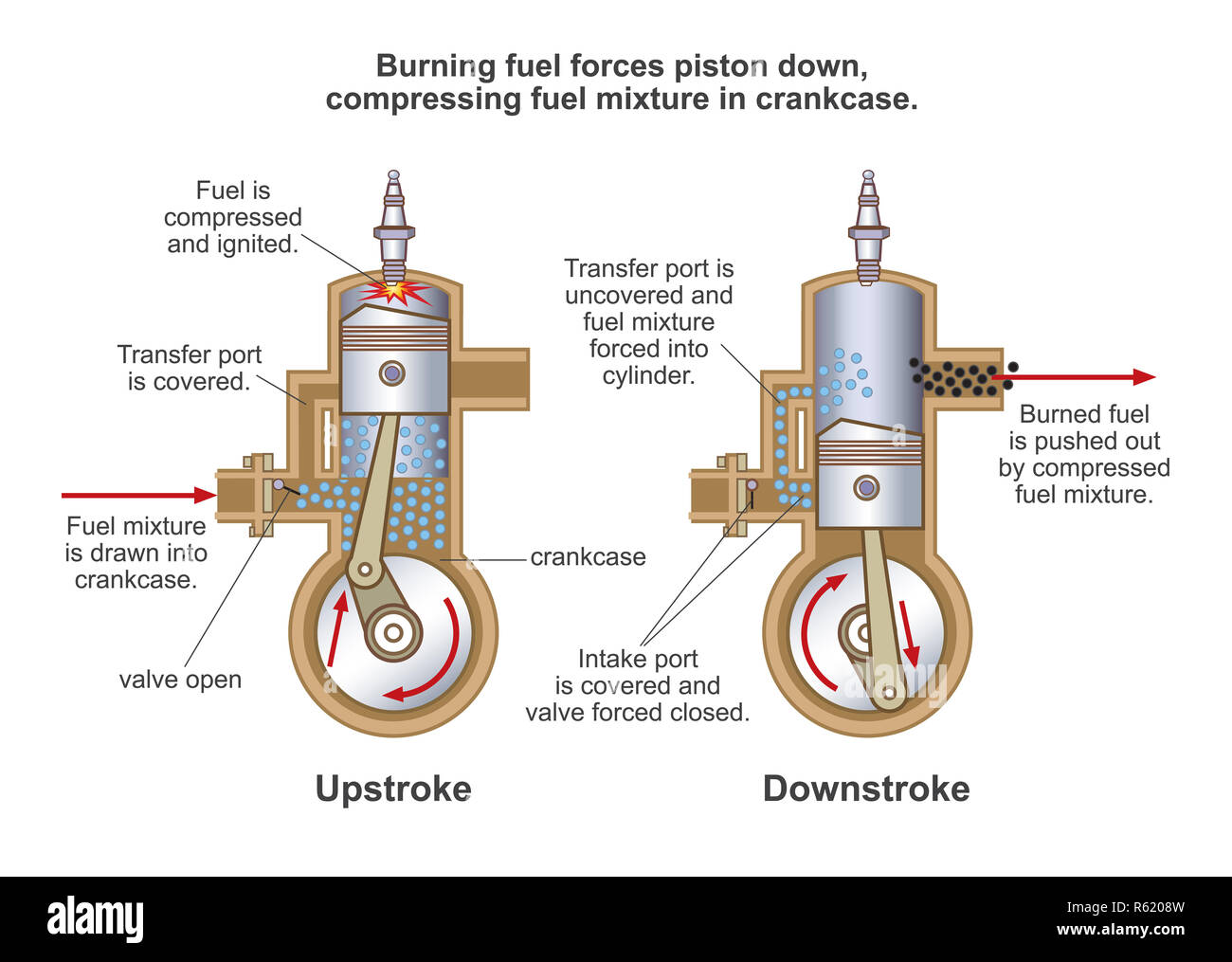
A c ombustion r evolution or c ombustion c ycle is the complete process of gas and air being sucked into the piston, igniting it, and expelling the exhaust: A s troke is when the piston moves from TDC to BDC, or vice versa. TDC is its position nearest to the valves, and BDC is its position furthest from them. The terms “top dead center” (TDC) and “bottom dead center” (BDC) refer to the piston’s position within the cylinder. In order to understand how these two engines are different, you first need to become familiar with the basics.ĭuring an engine’s combustion cycle, the piston moves up and down within the cylinder. How Do Combustion Engines Work, and What Is A “Stroke” Anyways? While we’re sure you’ve at least heard these terms before, do you really know the difference between them? How do they work, and which is better? Read on to learn the answers! Automotive engines have transformed over the years, but two main gasoline powered combustion engine designs remain: the 2-stroke and the 4-stroke.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
